Offshore
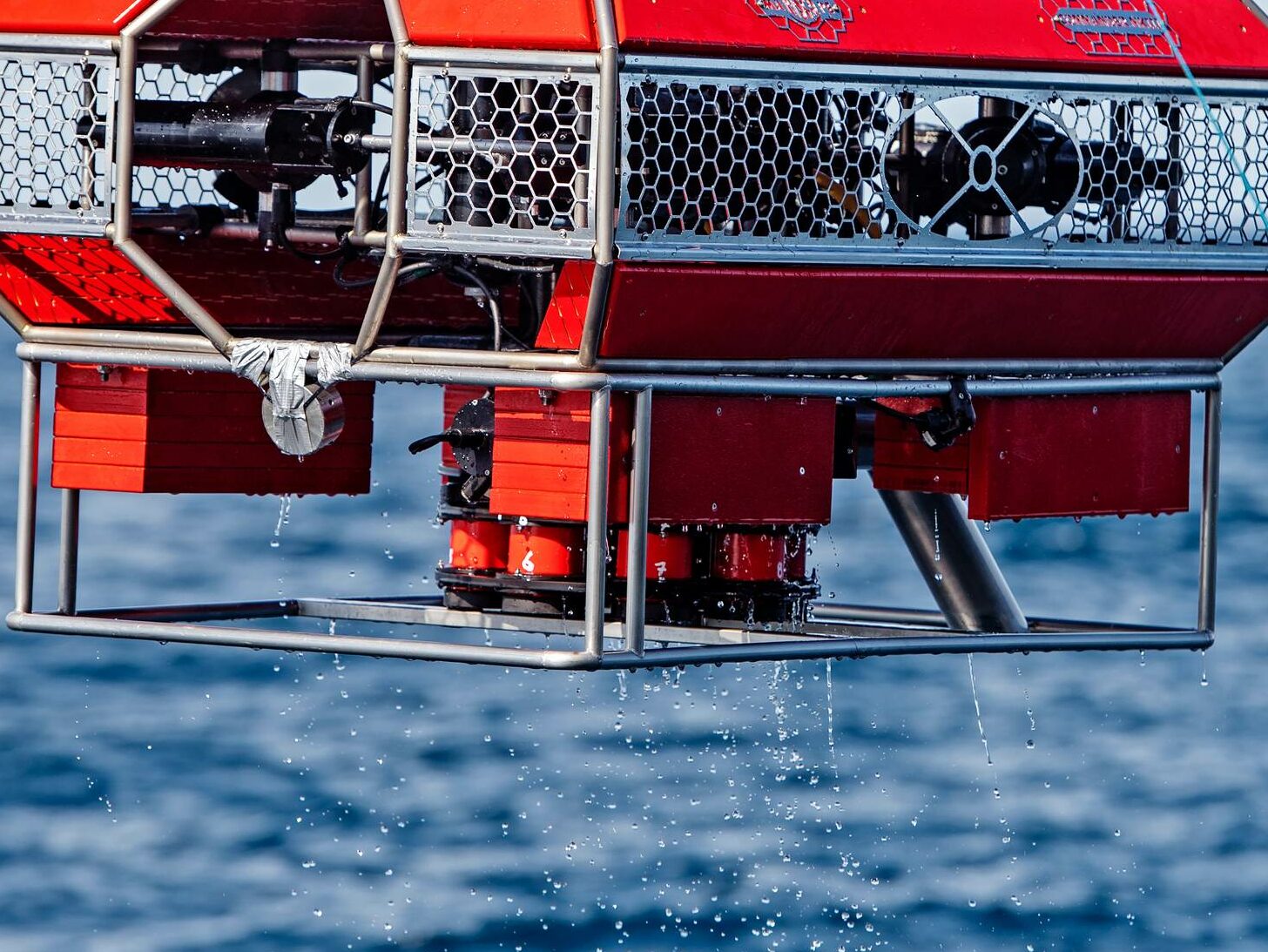
The ROV is used to navigate the ocean floor and gather data on the geology and topology of the seabed. The ROV is equipped with cameras, sonar, and other sensors that can provide detailed images of the seafloor, as well as data on the water temperature, salinity, and other environmental conditions.
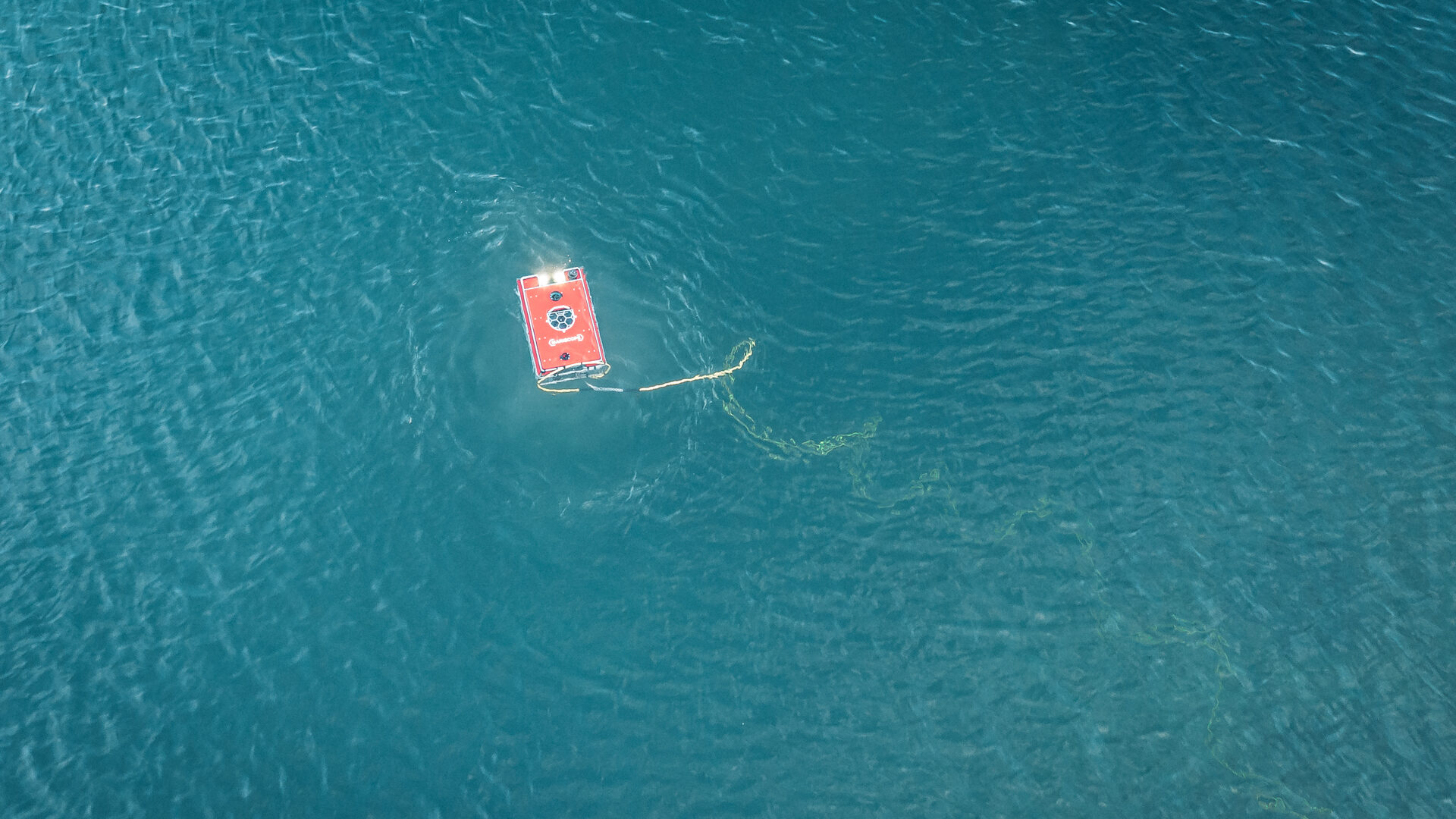
The dropcam is a camera that is dropped from the vessel to the ocean floor. It stays at the bottom of the ocean for some hours and then comes back to surface with the images and data recorded.
The towed system is a set of instruments and sensors that are towed behind the vessel to collect data on the water column, including the depth, temperature, and salinity of the water. This information can be used to create detailed maps of the ocean floor and to identify potential areas for exploration.
The data gathered by the ROV, dropcam, and towed systems is analyzed to identify potential oil and gas reserves or other valuable resources. Once these areas have been identified, exploratory drilling may be conducted to confirm the presence of the reserves.
Overall, offshore exploration with ROVs, dropcams, and towed systems is a critical service that helps to identify potential resources beneath the ocean floor. By using advanced technology to gather data on the geology and topology of the seafloor, as well as the water column, exploration teams can identify potential areas for further study and drilling. This helps to ensure the ongoing productivity of the oil and gas industry, while also supporting the development of other valuable resources that can contribute to the global economy.